(单词翻译:单击)
听力文本
Google AI System Could Improve Breast Cancer Detection
A Google artificial intelligence system was as good as expert radiologists at discovering which women had breast cancer in a new study. The system made the findings from thousands of mammogram images, researchers in the United States and Britain reported.
This is the newest study to show that artificial intelligence, or AI, may improve the accuracy of mammograms. Breast cancer affects one in eight women around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature.
The American Cancer Society says radiologists miss about 20 percent of breast cancers in mammograms. And many women who get the tests have a false positive result at some point. A false positive result shows a woman with cancer even though she does not have it.
The findings of the study were developed with DeepMind AI, which joined with Google Health in September.
The study results represent a big step toward the possibility of early breast cancer detection, said Mozziyar Etemadi. He is one of the study writers and based at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
The team included researchers at Imperial College London and Britain's National Health Service. Together, they trained the AI system to identify breast cancers on tens of thousands of mammograms.
They then compared the AI system's performance with the actual results from a set of 25,856 mammograms in the United Kingdom and 3,097 from the United States.
The study showed the AI system could identify cancers with a similar level of accuracy to expert radiologists. At the same time, it reduced the number of false positive results by 5.7 percent in the American patients and 1.2 percent in the British patients.
It also cut the number of false negatives, where tests are wrongly listed as normal, by 9.4 percent in the American group, and 2.7 percent in the British group.
These results show differences in how mammograms are read. In the U.S., only one radiologist reads the results and the tests are done every one to two years. In Britain, the tests are done every three years, and each is read by two radiologists. When they disagree, a third radiologist reads it.
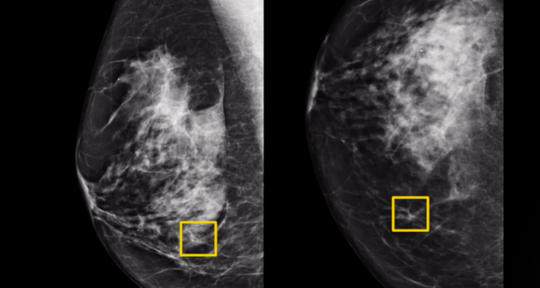
Seeing the signs
In a separate test, the researchers put the AI system against six radiologists and found it performed better at correctly detecting breast cancers.
Connie Lehman is chief of the breast imaging department at Harvard's Massachusetts General Hospital. She said the results agree with findings from many groups using AI to improve cancer detection in mammograms, including her own work.
The idea of using computers to improve cancer detection has been around for years. And computer-aided detection or CAD systems are common in mammography health centers, but CAD has not improved performance in health practice.
The issue, Lehman said, is that current CAD programs were trained to identify things human radiologists can see. But with AI, computers learn to find cancers based on the actual results of thousands of mammograms. So AI has the possibility of going beyond human ability to identify small signs the human eye and brain cannot.
Mozziyar Etemadi added that the study has shown, in tens of thousands of mammograms, that AI can "make a very well-informed decision."
A few limitations
The study has some limitations. Most of the tests were done using the same type of imaging equipment, and the U.S. group had a lot of patients with confirmed breast cancers.
Importantly, the team has not yet shown that the tool improves patient care, said Dr. Lisa Watanabe. She is chief medical officer of CureMetrix, a company whose AI mammogram program won U.S. approval last year.
She noted that AI is only helpful if it creates noticeable progress for radiologists.
Etemadi agreed that those studies are needed, as is regulatory approval, a process that could take many years.
I'm Alice Bryant.
重点解析
重点讲解:
1. even though 即使;尽管;纵然;
Many doctors fail to report cases, even though food poisoning is a notifiable disease.
很多医生没有报告病例,尽管食物中毒是应该通报的。
2. at the same time 同时;
She looked so beautiful, and at the same time so remote.
她相貌如此美丽,同时又如此清高不群。
3. agree with 同意;赞成;意见一致;
Your account of the accident does not agree with hers.
你对事故的叙述与她的叙述不一致。
4. be based on 以…为基础;
The reports were based on inaccurate information.
这些报告所依据的是不准确的信息。
参考译文
谷歌人工智能系统可以提高乳腺癌检测的准确性
在一项新研究中,谷歌人工智能系统在发现女性乳腺癌方面的表现与专业放射科医生一样好。美国和英国的研究人员报告称,该系统从数千张乳房X光检查图像中得出了结果。
这是表明人工智能(简称AI)可以提高乳房X光检查准确性的最新研究。乳腺癌影响全球八分之一的女性。这项研究发表在《自然》期刊上。
美国癌症学会表示,放射科医生在乳房X光检查中错过了约20%的乳腺癌。许多接受检查的女性有时会得到假阳性结果。该结果显示女性患有乳腺癌,但其实并没有。
研究发现由DeepMind AI部门完成,该部门于去年9月加入谷歌健康。
莫伊亚·埃特马迪表示,研究结果表明乳腺癌早期检测的可能性迈出了重要一步。他是这项研究的作者之一,就职于芝加哥的西北医学。
研究团队包括伦敦帝国理工学院和英国英国国家健康体系的研究人员。他们一起训练人工智能系统识别数万张乳房X光检查图像中的乳腺癌。
他们将这个人工智能系统的表现与美国3097张乳房X光照片和英国25856张乳房X光照片的实际结果进行了比较。
研究表明,人工智能系统识别癌症的准确率与专业放射科医生的相似。与此同时,人工智能系统分别将美国患者和英国患者的假阳性结果减少了5.7%和1.2%。
这一系统还减少了检查中被错列为无病的假阴性率,美国组减少了9.4%,英国组减少了2.7%。
这些结果表明乳房X光检查的辨别方式存在不同。在美国,只有一名放射科医生判断结果,检查每一到两年进行一次。而在英国,检查每三年进行一次,结果由两名放射科医生研读。当二人意见不一致时,会交由第三名放射科医生判断。
发现迹象
在另一项测试中,研究人员让人工智能系统对阵六名放射科医生,结果表明,人工智能系统在检测乳腺癌的准确率方面更胜一筹。
康妮·雷曼是哈佛大学医学院附属麻省总医院的乳腺影像科负责人。她说,这项研究的结果与许多小组的研究结果相符,包括她自已在内,这些小组用人工智能技术来提高乳房X光图像中的癌症检测率。
用计算机来提高癌症检测率的想法已经存在很多年了。计算机辅助检测或计算机辅助设计(简称CAD)系统在乳房X光照相术健康中心很常见,但CAD系统在临床实践中并未提高性能。
雷曼表示,问题是当前的CAD程序被训练成识别人类放射科医生可以看到的情况。但借助人工智能技术,计算机学会根据数千张乳房X光检查图像的实际结果来发现癌症。因此,人工智能有可能超越人类的能力来识别人眼和大脑无法感知的细微线索。
莫伊亚·埃特马迪补充说,这项研究通过数万张乳房X光照片证明,人工智能可以“做出非常明智的决定”。
一些局限
这项研究存在一些局限性。大多数检查是用同类型的成像设备进行的,而且美国组有许多已确诊为乳腺癌的患者。
渡边丽莎博士表示,重要的是,研究团队尚未证明这一工具能改善患者护理。她是CureMetrix公司的首席医疗官,该公司的人工智能乳房X光成像程序去年获得了美国的批准。
她指出,人工智能只有在为放射科医生带来显著进步时才有用。
埃特马迪同意需要进行这些研究,同时也需要获得监管批准,这一过程可能需要数年时间。
爱丽丝·布莱恩特报道。
译文为可可英语翻译,未经授权请勿转载!


